Vulcanisation
Vulcanisation is the last step in processing natural rubber mixtures. Natural materials turn into elastic rubber at this point, and they get their final geometric shape and technical properties.Pressing technology is the oldest, quite a frequently used method in rubber product manufacturing. The electronically heated vulcanising plates transmit heat to the product. Depending on the product to be manufactured, time can alter and 4-6 N/mm2 pressure is used. After opening the mould, the product can be removed. Minute regulation of temperature is provided by a high precision device.
Compression means putting the prepared raw material into a hot and open mould. Then mould parts are joined, put into the vulcanising press where it fills the cavities of the mould. Excess material flows into the separating rails and turns into flash. In order to fill the cavities fully, an excess pressure of 10-15% should be applied, thus flash is formed, too. Manual flashing can be done by a pair of scissors, a knife, a grinding machine or a tool. Mechanical flashing is much more accurate and efficient than the manual one. Grinding or piercing can help remove flash. Cycle time of vulcanisation depends on the time of vulcanisation, on treatment time of pressing and on tools. In order to reduce vulcanisation time and perform economically it is recommended that we use the highest temperature possible. At a certain mould, temperature dependence of shrinking should be taken into account because of the change in size of the product.
The compression process has the advantage that producing smaller sets is more economical than other procedures. Tools can be created by using special metal chipping methods.

600x600 rubber industry pressing machine

Vulcanised rubber components

Tube compensator
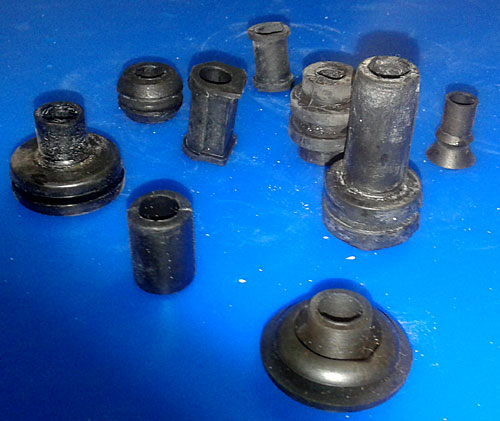

Grommets, rubber mountings and vacuum rubber
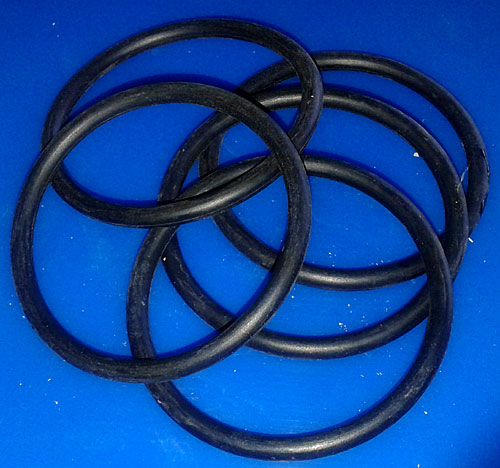

O-rings

Stuffing, rubber mountings